
After the general elections last year, Türkiye’s monetary policy shift has lessened the likelihood of a more severe balance-of-payments crisis. If maintained, the current policy could enhance credit fundamentals.
Scope Ratings updated Türkiye's rating Outlook to Stable from Negative on 12 January, citing the adoption of more traditional policies post the May 2023 general elections. The Central Bank of the Republic of Türkiye's shift towards consistently tighter monetary policy to address double-digit inflation has bolstered its credibility and ameliorated prior damage to the country's reputation for prudent economic management.
The series of interest-rate hikes and targeted credit tightening measures have begun to curtail credit expansion and private spending, consequently reducing the current account deficit and external gross financing requirements. Scope projects these financing needs to amount to USD 250 billion in 2024, approximately 19% of GDP. Meeting these requirements should also become easier as improved foreign investor sentiment results in capital inflows. Additionally, the Ministry of Treasury and Finance aims to secure USD 10 billion in external funding in 2024.
Another positive outcome of the tighter monetary policy is the recovery of Türkiye’s gross international reserves, excluding gold, which increased from USD 55.7 billion in May 2023 to USD 92.8 billion in December (Figure 1). Nonetheless, the international reserves still fall short of covering gross external financing needs.
Figure 1. Shift in monetary policy leads to a revival in critically low international reserves
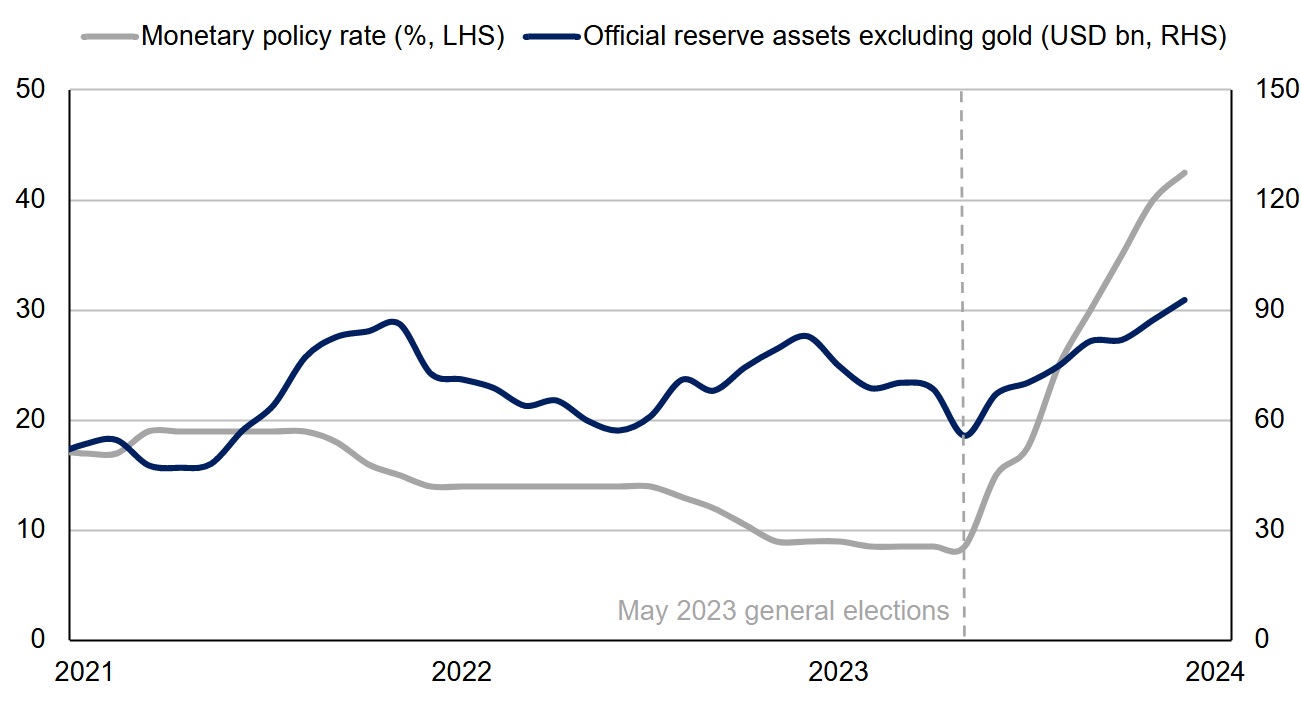
Source: CBRT, Scope Ratings
If the CBRT maintains its recent orthodox policy approach, we anticipate a gradual rebalancing of Türkiye’s economy, leading to enhanced resilience against external shocks. However, significant external and financial risks persist until more headway is made in reducing inflation. The lack of commitment to uphold a specific exchange rate for the lira has contributed to these lingering challenges.
Despite a robust economic growth, conditions are expected to tighten this year, partially offset by post-earthquake reconstruction efforts. Anticipated real GDP growth for 2024 is 3.3%, representing a moderate decline from the 4.1% recorded in 2023.
GDP growth is predicted to slightly decrease as stricter funding conditions counterbalance the reconstruction efforts following the February 2023 earthquake. It is expected that the real GDP growth will reach 3.3% in 2024, down from 4.1% in 2023.
President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan has shown public support for the central bank's policies, even though he previously contended that low interest rates would help in curbing inflation. However, a more severe-than-anticipated economic slowdown resulting from external shocks or heightened geopolitical tensions could challenge the sustainability of the recent move towards policy normalization.
The government's dedication to orthodox economic policies in the lead-up to the local elections in March will serve as a crucial trial as the economy slows under the impact of the recent months' tighter monetary policy. In a stressed scenario, interference in monetary decisions by political entities might resurface, escalating the risk of policy reversals and reducing the potential for further progress in reducing inflation and rebalancing the economy. Decision-making remains highly concentrated, and independent institutions are frequently influenced by politics. Reports of the government's crackdown on internet access before the local elections also raise concerns.
The risk of errors in the adjustment of policy normalization and/or reversals constrains Türkiye’s long-term foreign-currency ratings at B- due to the country’s ongoing external and financial vulnerabilities.

Subscribe to our daily newsletter and get the best forex trading information and markets status updates
Trade within minutes!
Comment (0)